Cat: MF-1005
Cat: MF-1005
IL5, Mouse, HEK293 Cells,Tag Free: Product Information
P04401
Human embryonic kidney cell, HEK293-derived mouse IL-5 protein
Met21-Gly133
13.1 kDa
Solution protein.
Dissolved in sterile PBS buffer. This solution can be diluted into other aqueous buffers. Centrifuge the vial prior to opening.
Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
Shipping with dry ice
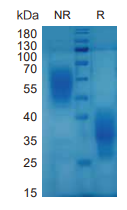
> 95%, determined by SDS-PAGE
<0.010 EU per 1 ug of the protein by the LAL method
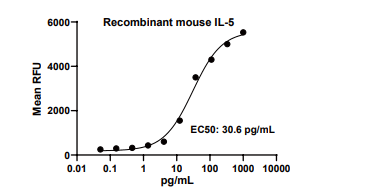
Measured in a cell proliferation assay using TF-1 human erythroleukemic cells. The EC50 for this effect is 17-35.6 pg/mL.
IL5, Mouse, HEK293 Cells,Tag Free:SDS-PAGE & Bioactivity
IL5, Mouse, HEK293 Cells,Tag Free:Synonyms
IL5; IL-5; IL-5T-cell replacing factor; interleukin 5 (colony-stimulating factor, eosinophil); interleukin-5
IL5, Mouse, HEK293 Cells,Tag Free:Background
Interleukin-5 (IL-5) is a secreted glycoprotein that belongs to the alpha -helical group of cytokines (1 - 3). Unlike other family members, it is present as a covalently linked antiparallel dimer (4, 5). The cDNA for mouse IL-5 encodes a signal peptide and a 113 amino acid (aa) mature protein. Mature
mouse IL-5 shares 70%, 94%, 58%, 66%, 59% and 63%, aa sequence identity with human, rat, canine, equine, feline and porcine IL-5, respectively, and shows cross-reactivity with human IL-5 receptor. IL-5 is primarily produced by CD4+ Th2 cells, but also by activated eosinophils, mast cells,
EBV-transformed B cells, Reed-Sternberg cells in Hodgkin’s disease, and IL-2-stimulated invariant natural killer T cells (iNKT) (1 - 3, 6 - 8). IL-5
increases production and mobilization of eosinophils and CD34+ progenitors from the bone marrow and causes maturation of eosinophil precursors
outside the bone marrow (1, 6, 9, 10). The receptor for human IL-5, mainly expressed by eosinophils, but also found on basophils and mast cells,
consists of a unique ligand-binding subunit (IL-5 R alpha ) and a shared signal-transducing subunit, beta c (3, 6, 11). IL-5 R alpha first binds IL-5 at low affinity, then associates with preformed beta c dimers, forming a high-affinity receptor (12).
1. Rosenberg, H. F. et al. (2007) J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 119:1303.
2. Elsas, P.X. and M. I. G. Elsas (2007) Curr. Med. Chem. 14:1925.
3. Martinez-Moczygemba, M. and D. P. Huston (2003) J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 112:653.
4. Minamitake, Y. et al. (1990) J. Biochem. 107:292.
5. McKenzie, A. N. et al. (1991) Mol. Immunol. 28:155.
6. Shakoory, B. et al. (2004) J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 24:271.
7. Lalani, T. et al. (1999) Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 82:317.
8. Sakuishi, K. et al. (2007) J. Immunol. 179:3452.
9. Clutterbuck, E. J. et al. (1989) Blood 73:1504.
10. Cameron, L. et al. (2000) J. Immunol. 164:1538.
11. Tavernier, J. et al. (1991) Cell 66:1175.
12. Zaks-Zilberman, M. et al. (2008) J. Biol. Chem. 283:13398.