Cat: HF-1028B
Cat: HF-1028B
IL28B, Human, HEK293 Cells,Tag Free: Product Information
interleukin-28B; IFN-lambda 3; IL28B; IL-28B; IL28C; interferon, lambda 3
AAN28264
Human embryonic kidney cell, HEK293-derived human IL-28B/IFN-lambda 3 protein Arg30-Val200
19.6 kDa
Solution protein.
Dissolved in sterile PBS buffer. This solution can be diluted into other aqueous buffers. Centrifuge the vial prior to opening.
Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
Shipping with dry ice.
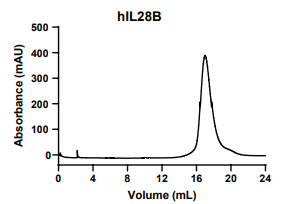
> 95%, determined by SDS-PAGE
<0.010 EU per 1 ug of the protein by the LAL method
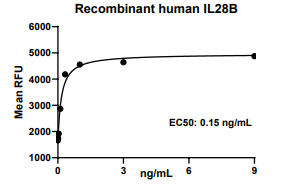
Measured in an anti-viral assay using HepG2 human hepatocellular carcinoma cells infected with encephalomyocarditis (EMC) virus. The EC50 for this effect is 0.1-0.5 ng/mL.
IL28B, Human, HEK293 Cells,Tag Free:SDS-PAGE & Bioactivity
IL28B, Human, HEK293 Cells,Tag Free:Synonyms
interleukin-28B; IFN-lambda 3; IL28B; IL-28B; IL28C; interferon, lambda 3
IL28B, Human, HEK293 Cells,Tag Free:Background
Interleukin-28B(also named interferon-lambda 3, IFN-lambda 3), IL-28A (IFN-lambda 2) and IL-29 (IFN-lambda 1) are type III interferons that are class II cytokine receptor ligands (1-4). They are distantly related to members of the IL-10 family and type I IFN family (1- 4). Human IL-28B cDNA encodes a 200 amino acid (aa) protein with a 25 aa signal peptide and a 175 aa mature protein that lacks N-glycosylation sites. Mature human IL-28B shares 64% and 75% aa sequence identity with mouse and canine IL-28B, respectively, and is active across species (5). Human IL-28B shares 94% and 69% aa identity with human IL -28A and IL-29, respectively (4). Type III interferons are widely expressed, but are mainly produced by antigen presenting cells in response to viruses and double -stranded RNA that interact with Toll-like receptors or RIG-1 family helicases (2-6). They signal through a widely expressed receptor that is a heterodimer of the IL-10 receptor beta (IL-10 R beta ) and IL-28 receptor alpha (IL-28 R alpha ; also called IFN-lambda R1) (2, 3, 7, 9). Interaction of either type I or type III IFNs with their receptors activates similar pathways, including JAK tyrosine kinase activation, STAT phosphorylation and formation of the IFN-stimulated regulatory factor 3 (ISGF-3) transcription factor complex (1-3). Both type I and III IFNs induce anti-viral activity and up-regulate MHC class I antigen expression (2-6). Cell l ines responsive to type III IFNs are also responsive to type I IFNs, but in general, higher concentrations of type III IFNs are needed for similar in vitro responses (8). In vivo, however, type III IFNs enhance levels of IFN-gamma in serum, suggesting that the robust anti-viral activity of type III IFNs may stem in part from activation of the immune system (5, 7). Anti-proliferative and antitumor activity in vivo has also been shown for type III IFNs (9-11).
1. Chen, Q. et al. (2006) Vitam. Horm. 74:207.
2. Sheppard, P. et al. (2003) Nat. Immunol. 4:63.
3. Kotenko, S.V. et al. (2003) Nat. Immunol. 4:69.
4. Bartlett, N.W. et al. (2005) J. Gen. Virol. 86:1589.
5. Ank, N. et al. (2006) J. Virol. 80:4501.
6. Onoguchi, K. et al. (2007) J. Biol. Chem. 282:7576.
7. Siebler, J. et al. (2007) Gastroenterology 132:358.
8. Meager, A. et al. (2005) Cytokine 31:109.
9. Lasfar, A. et al. (2006) Cancer Res. 66:4468.
10. Sato, A. et al. (2006) J. Immunol. 176:7686.
11. Zitzmann, K. et al. (2006) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 344:1334.