Cat: HF-2047
Cat: HF-2047
PLGF-Ab2, Human, HEK293 Cells,Tag Free: Product Information
Q07326
Human embryonic kidney cell, HEK293-derived human PIGF protein
Ala21-Arg149
14.5 kDa
Solution protein.
Dissolved in sterile PBS buffer .
This solution can be diluted into other aqueous buffers. Centrifuge the vial prior to opening
Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
Shipping with dry ice.
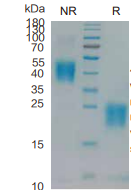
> 95%, determined by SDS-PAGE.
<0.010 EU per 1 ug of the protein by the LAL method.
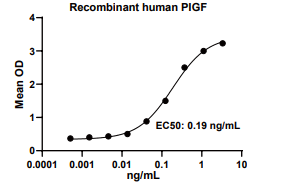
Measured by its binding ability in a functional ELISA. When Recombinant Human VEGF R1/Flt-1 Fc Chimera is immobilized at 0.5 μg/mL, 100 μL/well, the concentration of Recombinant Human PlGF that produces 50% of the optimal binding response is approximately 0.05-1 ng/mL.
PLGF-Ab2, Human, HEK293 Cells,Tag Free:Synonyms
PlGF; PlGF-2; PLGFplacental growth factor-like; PGFL; placenta growth factor; placental growth factor
PLGF-Ab2, Human, HEK293 Cells,Tag Free:Background
Placenta growth factor (PlGF) is a member of the PDGF/VEGF family of growth factors that share a conserved pattern of eight cysteines (1, 2).
Alternative splicing results in at least three human mature PlGF forms containing 131 (PlGF-1), 152 (PlGF-2), and 203 (PlGF-3) amino acids (aa)
respectively (1, 2). Only PlGF-2 contains a highly basic heparin-binding 21 aa insert at the C-terminus (1). Human PlGF-1 shares 56%, 55%, 74% and
95% aa identity with the comparable isoform of mouse, rat, canine, and equine PlGF, respectively. PlGF is mainly found as variably glycosylated, secreted,
55-60 kDa disulfide linked homodimers (3). Mammalian cells expressing PlGF include villous trophoblasts, decidual cells, erythroblasts, keratinocytes, and some endothelial cells (1, 4-6). Circulating PlGF increases during pregnancy, reaching a peak in mid-gestation; this increase is attenuated in preeclampsia
(7). However, deletion of PlGF in the mouse does not affect development or reproduction. Postnatally, mice lacking PlGF show impaired angiogenesis in
response to ischemia (8).PlGF binds and signals through VEGF R1/Flt-1 but not VEGF R2/Flk-1/KDR, while VEGF binds both but signals only through the angiogenic receptor, VEGF R2. PlGF and VEGF therefore compete for binding to VEGF R1, allowing high PlGF to discourage VEGF/VEGF R1 binding and promote VEGF/VEGF R2-mediated angiogenesis (1, 4, 8, 9). However, PlGF (especially PlGF-1) and some forms of VEGF can form dimers that decrease the angiogenic effect of VEGF on VEGF R2 (3, 4). PlGF-2, but not PLGF-1, shows heparin-dependent binding of Neuropilin (Npn)-1 and Npn-2 (10, 11).
1. Hauser, S. and H.A. Weich (1993) Growth Factors 9:259.
2. Maglione, D. et al. (1993) Oncogene 8:925.
3. Eriksson, A. et al. (2002) Cancer Cell 1:99.
4. Ribatti, D. (2008) Angiogenesis 11:215.
5. Oura, H. et al. (2003) Blood 101:560.
6. Roncal, C. et al. (2010) Cardiovasc. Res. 86:29
7. Levine, R.J. et al. (2004) N. Engl. J. Med. 350:672.
8. Carmeliet, P. et al. (2001) Nat. Med. 7:575.
9. Autiero, M. et al. (2003) Nat. Med. 9:936.
10. Migdal, M. et al. (1998) J. Biol. Chem. 273:22272.
11. Cheng, L. et al. (2004) J. Biol. Chem. 279:30654.