Cat: HF-2048
Cat: HF-2048
CCL2, Human, HEK293 Cells,Tag Free: Product Information
P13500
Human embryonic kidney cell, HEK293-derived human CCL2/MCP-1 proteinGln24-Thr99
8.7 kDa
Solution protein.
Dissolved in sterile PBS buffer .
This solution can be diluted into other aqueous buffers. Centrifuge the vial prior to opening
Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
Shipping with dry ice.
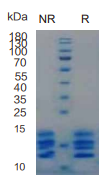
> 95%, determined by SDS-PAGE
<0.010 EU per 1 ug of the protein by the LAL method
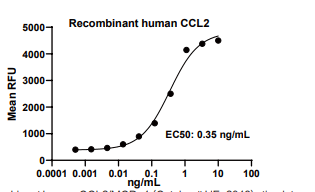
Measured by its ability to chemoattract BaF3 mouse pro-B cells transfected with human CCR2A. The EC50 for this effect is 0.1-1 ng/mL
CCL2, Human, HEK293 Cells,Tag Free:SDS-PAGE & Bioactivity
CCL2, Human, HEK293 Cells,Tag Free:Synonyms
CCL2; GDCF-2; HC11; HSMCR30; MCAF; Mcp1; MCP-1; SCYA2; SMC-CF
CCL2, Human, HEK293 Cells,Tag Free:Background
CCL2, also called monocyte chemotactic protein-1 (MCP-1) or JE, is a member of the C-C or beta chemokine family that is best known as a chemotactic agent for mononuclear cells (1, 2). Human CCL2 cDNA encodes a 99 amino acid (aa) precursor protein with a 23 aa signal peptide and a 76 aa mature
protein (2). Removal of the first 5 aa of the mature protein, including the N-terminal pyrrolidone carboxylic acid-modified glutamine, occurs naturally by
metalloproteinase cleavage and down-regulates activity but not receptor binding (3). CCL2 may form multiple bands from 8.7-13.5 kDa on SDS-PAGE
due to non-covalent dimerization and variable carbohydrate content (3). Mature human CCL2 shares 78-79% aa identity with canine, porcine and equine CCL2, while mouse and rat express a form of CCL2 that is extended by 49 aa and shares only ~56% aa identity within the common region. Human CCL2
can, however, induce a response in murine cells (4). Fibroblasts, glioma cells, smooth muscle cells, endothelial cells, lymphocytes and mononuclear
phagocytes can produce CCL2 either constitutively or upon mitogenic stimulation, but monocytes and macrophages appear to be the major source (1, 2).
In addition to its chemotactic activity, CCL2 induces enzyme and cytokine release by monocytes, NK cells and lymphocytes, and histamine release by
basophils that express its receptor, CCR2 (2). Additionally, it promotes Th2 polarization in CD4+ T cells (5). CCL2-mediated recruitment of monocytes to
sites of inflammation is proposed to play a role in the pathology of atherosclerosis, multiple sclerosis and allergic asthma (6, 7).
1. Yoshimura, T. et al. (1989) FEBS Lett. 244:487.
2. Deshmane, S.L. et al. (2009) J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 29:313.
3. Proost, P. et al.(1998) J. Immunol. 160:4034.
4. Ju Lee, H. et al. (2015) J. Immunol. 194:3634.
5. Luther, S.A. and J.G. Cyster (2001) Nat. Immunol. 2:102.
6. Daly, C. et al. (2003) Microcirculation 10:247.
7. Aukrust, P. et al. (2008) Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 28:1909.