Cat: HF-2009
Cat: HF-2009
IFNA8, Human, HEK293 Cells,Tag Free: Product Information
P32881
Human embryonic kidney cell, HEK293-derived human IFN-alpha 8/IFNA8 protein
Cys24-Glu189
19.5 kDa
Solution protein.
Dissolved in sterile PBS buffer. This solution can be diluted into other aqueous buffers. Centrifuge the vial prior to opening.
Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
Shipping with dry ice
> 95%, determined by SDS-PAGE
<0.010 EU per 1 ug of the protein by the LAL method
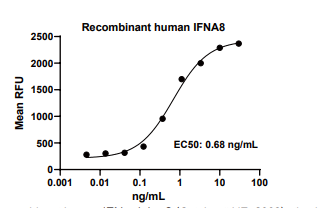
Measured in anti-viral assays using HeLa human cervical epithelial carcinoma cells infected with encephalomyocarditis (EMC) virus. The EC50 for this effect is 0.2-5 ng/mL.
IFNA8, Human, HEK293 Cells,Tag Free:SDS-PAGE & Bioactivity
IFNA8, Human, HEK293 Cells,Tag Free:Synonyms
IFNA8; IFN-alpha 8; IFNalpha B2; IFN-alpha B2; IFN-alpha-8; IFN-alphaB; interferon alpha type 201
IFNA8, Human, HEK293 Cells,Tag Free:Background
Interferon alpha 8 (IFNA8) also known as leukocyte interferon, represents a group of related but distinct proteins that share over 95% amino acid s equence homology. They are members of the type I interferon family which share a common cell surface receptor composed of two subunits, a 100 kDa ligand-binding subunit (IFN-alpha R2) and a 125 kDa ligand binding and signal transduction subunit (IFN-alpha R1) that is involved both in ligand binding and signal transduction. IFN-alpha has both anti-viral and immunomodulatory activities on target cells.Interferons (IFN) are a family of cytokines with potent antiviral, antiproliferative and immunomodulatory properties, classified based on their binding specificity to cell surface receptors (1). Human IFNA2 was originally cloned in the early ‘80s and now more than a dozen closely related IFN alpha subtypes have been identified in both the human and mouse genome, each sharing about 80% amino acid (aa) sequence homology (2-4). Structurally, type I IFNs belong to the class of five helical-bundle cytokines, with the IFNA subtypes containing 2 conserved disulfide bonds (5). The extracellular domain (ECD) of mature human IFNA8, also known as IFN-alpha B2, shares 60% aa sequence identity with mouse homolog. The type I IFNs bind to the interferon alpha receptor (IFNAR), which consists of two subunits: IFNAR1 (alpha-subunit) and IFNAR2 (beta -subunit) (6, 7). Individual IFNA subtypes are known to display unique efficacies to viral protection, and IFNA8 is the most potent IFNA, judging by both antiviral and antiproliferative activities (8).
1. Pestka, S. et al. (1987) Annu. Rev. Biochem. 56:727.
2. Goeddel, D.V. et al. (1980) Nature 287:411.
3. Matsumiya, T. et al. (2007) J. Immunol. 179:4542.
4. Schreiber, G. and J. Piehler (2015) Trends Immunol. 36:139.
5. Wittling, M.C. et al. (2021) Front Immunol. 11:605673.
6. van Pesch, V. et al. (2004) J. Virol. 78:8219.
7. James, C.M. et al. (2007) Vaccine. 25(10):1856.
8. Slutzki, M. et al. (2006) J Mol Biol. 360:1019.