Cat: HF-2015
Cat: HF-2015
TNF-alpha, Human, HEK293 Cells,Tag Free: Product Information
P01375
Human embryonic kidney cell, HEK293-derived human TNF-alpha proteinVal77-Leu233
17.4 kDa (Monomer)
Trimer in solution
Solution protein.
Dissolved in sterile PBS buffer. This solution can be diluted into other aqueous buffers. Centrifuge the vial prior to opening.
Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
Shipping with dry ice.
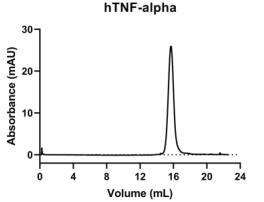
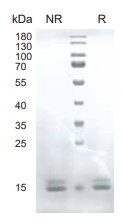
> 95%, determined by SDS-PAGE.
<0.010 EU per 1 ug of the protein by the LAL method.
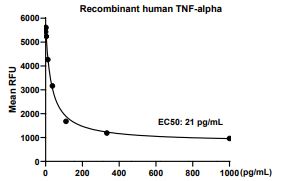
Measured in a cytotoxicity assay using L-929 mouse fibroblast cells in the presence of the metabolic inhibitor actinomycin D. The ED50 for this effect is 20-100 pg/mL.
TNF-alpha, Human, HEK293 Cells,Tag Free:SDS-PAGE & Bioactivity
TNF-alpha, Human, HEK293 Cells,Tag Free:Synonyms
Human Tumor Necrosis Factor alpha, rTNFA; TNF-A; TNFalpha
TNF-alpha, Human, HEK293 Cells,Tag Free:Background
Tumor necrosis factor alpha(TNF-alpha), is a pleiotropic pro-inflammatory cytokine secreted by various cells, including adipocytes, activated
monocytes, macrophages, B cells, T cells and fibroblasts (1,2). It belongs to TNF family of ligands, and signals through two receptors, TNFR1 and TNFR2. Human TNF-alpha consisits of a 35 amino acid (aa) cytoplasmic domain, a 21 aa transmembrane segment, and a 177 aa extracellular domain (ECD) (3).
The ECD of human TNF-alpha shares 97% aa sequence identity with rhesus and 71%-92% with bovine, canine, cotton rat, equine, feline, mouse, porcine, and rat TNF-alpha. TNF-alpha is assembled intracellularly to form a noncovalently linked homotrimer which is expressed on the cell surface (4). Cell
surface TNF-alpha can induce the lysis of neighboring tumor cells and virus infected cells, and it can generate its own downstream cell signaling following
ligation by soluble TNFR1 (2, 5). Shedding of membrane bound TNF-alpha by TACE/ADAM17 releases the bioactive cytokine, a 55 kDa soluble trimer of
the TNF-alpha extracellular domain (6-8). TNF-alpha binds the ubiquitous 55-60 kDa TNFR1(9, 10) and the hematopoietic cell-restricted 80 kDa TNFR2 (11, 12), both of which are also expressed as homotrimers (1, 2, 13).
1. Zelova, H. and J. Hosek (2013) Inflamm. Res. 62:641.
2. Juhasz, K. et al. (2013) Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 9:335.
3. Pennica, D. et al. (1984) Nature 312:724.
4. Tang, P. et al. (1996) Biochemistry 35:8216.
5. Perez, C. et al. (1990) Cell 63:251.
6. Black, R.A. et al. (1997) Nature 385:729.
7. Moss, M.L. et al. (1997) Nature 385:733.
8. Gearing, A.J.H. et al. (1994) Nature 370:555.
9. Schall, T.J. et al. (1990) Cell 61:361.
10. Loetscher, H. et al. (1990) Cell 61:351.
11. Dembic, Z. et al. (1990) Cytokine 2:231.
12. Smith, C.A. et al. (1990) Science 248:1019.
13. Loetscher, H. et al. (1991) J. Biol. Chem. 266:18324.