Cat: HF-2018
Cat: HF-2018
FGF2, Human, HEK293 Cells,Tag Free: Product Information
P09038
Human embryonic kidney cell, HEK293-derived human FGF basic/FGF2/bFGF protein
Met134-Ser288
16.5 kDa
Solution protein.
Dissolved in sterile PBS buffer. This solution can be diluted into other aqueous buffers. Centrifuge the vial prior to opening.
Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
Shipping with dry ice
> 95%, determined by SDS-PAGE.
<0.010 EU per 1 ug of the protein by the LAL method.
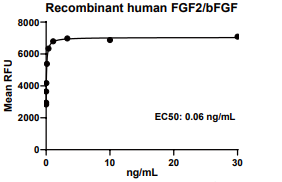
Measured in a cell proliferation assay using NR6R-3T3 mouse fibroblast cells. The EC50 for this effect is 0.01-0.1 ng/mL.
FGF2, Human, HEK293 Cells,Tag Free:SDS-PAGE & Bioactivity
FGF2, Human, HEK293 Cells,Tag Free:Synonyms
basic fibroblast growth factor bFGF; Basic fibroblast growth factor; bFGF; FGF basic; FGF2; FGF-2
FGF2, Human, HEK293 Cells,Tag Free:Background
FGF basic(FGF-2)is a member of the FGF superfamily of mitogenic proteins which show 35-60% amino acid conservation. FGF acidic and basic
are unique from other members of the family in that they lack classical secretory signal peptides. However, they are both readily secreted from cells by an alternative secretory pathway involving direct translocation and aided by several chaperones. FGF acidic (FGF-1) and FGF basic (FGF-2) were the first
two identified FGFs, and the designations acidic and basic refer to their relative isoelectric points. The full length human FGF basic protein is 288 amino
acids, but there are multiple start sites which produce various shorter forms. Further adding to the complexity, a variety of forms of FGF basic are produced as a result of N-terminal extensions. These extensions affect localization of FGF basic in cellular compartments but do not affect biological activity. FGF basic has been isolated from a number of sources, including neural tissue, adrenal cortex, pituitary gland, corpus luteum, and placenta. Binding of FGF to heparin or cell surface heparan sulfate proteoglycans is required for FGF binding with high affinity to FGF receptors. FGF basic stimulates proliferation of all cells of mesodermal origin as well as many cells of neuroectodermal, ectodermal, and endodermal origin. FGF basic also induces neuronal differentiation, survival, and regeneration, and modulates embryonic development and differentiation. These observed in vitro functions suggest FGF basic may play a
role in vivo in the modulation of such normal processes as angiogenesis, wound healing and tissue repair, embryonic development and differentiation, and neuronal function and neural degeneration. Additionally, FGF basic may also participate in the development of several pathological conditions resulting
from excessive cell proliferation and/or angiogenesis.
1. Coulier, F. et al. (1997) J. Mol. Evol. 44:43.
2. Chen, C.H. et al. (2004) Curr. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2:33.
3. Mohammadi, M. et al. (2005) Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 15:506.
4. Fernig, D. et al. (1994) Prog. Growth Factor Res. 5:353.