Cat: HF-2013
Cat: HF-2013
SCF, Human, HEK293 Cells,Tag Free: Product Information
P21583
Human embryonic kidney cell, HEK293-derived human SCF protein
Glu26-Ala189
18.5 kDa
Solution protein.
Dissolved in sterile PBS buffer. This solution can be diluted into other aqueous buffers. Centrifuge the vial prior to opening.
Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
Shipping with dry ice
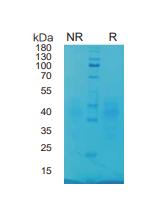
> 95%, determined by SDS-PAGE
<0.010 EU per 1 ug of the protein by the LAL method
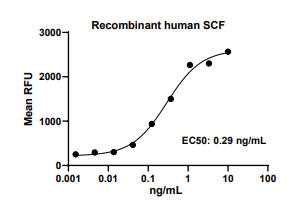
Measured in a cell proliferation assay using TF-1 human erythroleukemic cells. The EC50 for this effect is 0.1-3 ng/mL.
SCF, Human, HEK293 Cells,Tag Free:SDS-PAGE & Bioactivity
SCF, Human, HEK293 Cells,Tag Free:Synonyms
c-kit Ligand; DCUA; DFNA69; FPH2; FPHH; KIT ligand; Kitl; KITLG; KL-1; MGF; MGFSHEP7; SCF
SCF, Human, HEK293 Cells,Tag Free:Background
Stem cell factor (SCF) is a potent hematopoietic growth factor required in regulating both embryonic and adult hematopoiesis. SCF protein
promotes the survival, differentiation, and mobilization of multiple cell types including myeloid, erythroid, megakaryocytic, lymphoid, germ cell, and
melanocyte progenitors (1 7). SCF is a primary growth and activation factor for mast cells and eosinophils (8). And SCF assists in the recovery of cardiac function following myocardial infarction by increasing the number of cardiomyocytes and vascular channels (9). Stem cell factor is an important cytokine
for ex vivo clinical applications. Along with other cytokines, SCF is used in the culture and expansion of hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) as well as for
proliferation and differentiation of both myeloid and erythroid progenitor cells.Mature stem cell factor consists of a 189 amino acid (aa) extracellular
domain (ECD), a 23 aa transmembrane domain, and a 36 aa cytoplasmic tail (10).The ECD shows both N linked and O-linked glycosylation (11). SCF
protein exists in two forms, a membrane-bound form and a proteolytically processed soluble form that lacks the transmembrane domain and cytoplasmictail. The soluble form is created by proteolytic cleavage at two alternate sites in the extracellular juxtamembrane region releasing a 25 kDa soluble SCF
protein which is comparable to the only form produced by Steel-dickie mutant mice (12, 13). There is also an alternately spliced isoform of human SCF
that lacks 28 amino acids that encompasses the primary proteolytic recognition site (14).
1. Ashman, L.K. (1999) Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 31:1037.
2. Sette, C. et al. (2000) Int. J. Dev. Biol. 44:599.
3. Yoshida, H. et al. (2001) J. Invest. Dermatol. Symp. Proc. 6:1.
4. Erlandsson, A. et al. (2004) Exp. Cell Res. 301:201.
5. Kapur, R. et al. (2002) Blood 100:1287.
6. Wang, C.-H. et al. (2007) Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 27:540.
7. Bashamboo, A. et al. (2006) J. Cell Sci. 119:3039.
8. Reber, L. et al. (2006) Eur. J. Pharmacol. 533:327.
9. Kanellakis, P. et al. (2006) Cardiovasc. Res. 70:117.
10. Martin, F.H. et al. (1990) Cell 63:203.
11. Arakawa, T. et al. (1991) J. Biol. Chem. 266:18942.
12. Majumdar, M.K. et al. (1994) J. Biol. Chem. 269:1237.
13. Brannan, C.I. et al. (1991) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 88:4671.
14. Anderson, D.M. et al. (1991) Cell Growth Differ. 2:373.