Cat: HF-1009
Cat: HF-1009
IL9, Human, HEK293 Cells,Tag Free: Product Information
Human IL9; IL9; IL-9; interleukin 9; Cytokine P40; HP40
P15248
Human embryonic kidney cell, HEK293-derived human IL9 protein
Gln19-Ile144
14.1 kDa
Solution protein
Dissolved in sterile PBS buffer to a concentration of 0.2 mg/mL.
This solution can be diluted into other aqueous buffers. Centrifuge the vial prior to opening.
Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage.
12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
Shipping with dry ice.
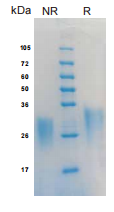
> 95%, determined by SDS-PAGE.
<0.010 EU per 1 ug of the protein by the LAL method.
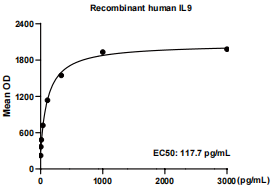
Measured in a cell proliferation assay using MO7e human megakaryocytic leukemic cells.
The EC50 for this effect is 100-200 pg/mL.
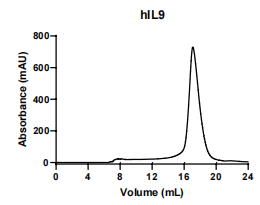
IL9, Human, HEK293 Cells,Tag Free:SDS-PAGE & Bioactivity
IL9, Human, HEK293 Cells,Tag Free:Synonyms
Human IL9; IL9; IL-9; interleukin 9; Cytokine P40; HP40
IL9, Human, HEK293 Cells,Tag Free:Background
Interleukin-9 (IL-9) ,also known as P40 and MEA (mast cell growth-enhancing activity), is a 30-40 kDa glycosylated member of a cytokine family that includes Interleukins-2, -4, -7, -15, and -21. These proteins utilize heteromeric receptors containing the Common gamma chain ( gamma c) in addition to ligand-specific subunits. IL-9 interacts selectively with IL-9 R which then associates with gamma c to form the functional receptor complex. IL-9 contributes to allergic inflammation, autoimmunity-induced inflammation, parasite clearance from the GI tract, and Treg-mediated immune suppression (1, 2). It enhances the expansion and recruitment of mast cells and eosinophils as well as the production of IgE and Th2 cytokines (3-6). It is required for anaphylactic responses to ingested allergens but not to systemic allergens (7). IL-9 plays multiple roles in the development and function of subsets within the CD4+ T cell lineage (8). It is expressed by activated Th9, Th17, Treg, and Th2 cells (3, 9-12). IL-9 acts as an autocrine growth and activation factor for Th17, Treg, and mast cells (3, 11, 13).
1.Noelle, R.J. and E.C. Nowak (2010) Nat. Rev. Immunol. 10:683.
2. Goswami, R. and M.H. Kaplan (2011) J. Immunol. 186:3283.
3. Nowak, E.C. et al. (2009) J. Exp. Med. 206:1653.
4. Townsend, M.J. et al. (2000) Immunity 13:573.
5. Leech, M.D. and R.K. Grencis (2006) J. Immunol. 176:2505.
6. Fawaz, L.M. et al. (2007) J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 120:1208.
7. Osterfeld, H. et al. (2010) J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 125:469.
8. Jabeen, R. and M.H. Kaplan (2012) Curr. Opin. Immunol. 24:303.
9. Tan, C. et al. (2010) J. Immunol. 185:6795.
10. Jager, A. et al. (2009) J. Immunol. 183:7169.
11. Elyaman, W. et al. (2009) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 106:12885.
12. Lu, L.-F. et al. (2006) Nature 442:997.
13. Stassen, M. et al. (2000) J. Immunol. 164:5549.