Cat: HF-1013
Cat: HF-1013
IL13, Human, HEK293 Cells,Tag Free: Product Information
Human IL13; interleukin-13; IL13; IL-13; interleukin 13; MGC116786
Human embryonic kidney cell, HEK293-derived human IL-13 protein Gly21-Asn132 13.3 kDa
13.3 kDa
Solution protein.
Dissolved in sterile PBS buffer.
This solution can be diluted into other aqueous buffers. Centrifuge the vial prior to opening.
Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage.12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
Shipping with dry ice
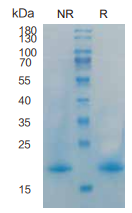
> 95%, determined by SDS-PAGE.
<0.010 EU per 1 ug of the protein by the LAL method.
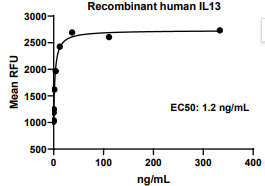
Measured in a cell proliferation assay using TF-1 human erythroleukemic cells. The EC50 for this effect is 0.5-2.0 ng/mL.
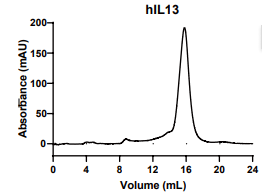
IL13, Human, HEK293 Cells,Tag Free:SDS-PAGE & Bioactivity
IL13, Human, HEK293 Cells,Tag Free:Synonyms
Human IL13; interleukin-13; IL13; IL-13; interleukin 13; MGC116786
IL13, Human, HEK293 Cells,Tag Free:Background
Interleukin-13 (IL-13) is a monomeric 17 kDa immunoregulatory cytokine that plays a key role in the pathogenesis of allergy, cancer, and tissue fibrosis. It is secreted by several helper T cell subsets, NK cells, mast cells, eosinophils, basophils, and visceral smooth muscle cells (1-3). Mature human IL-13
shares approximately 58% amino acid sequence identity with mouse and rat IL-13. Despite the low homology, it exhibits cross-species activity between
human, mouse, and rat (4). IL-13 suppresses the production of proinflammatory cytokines and other cytotoxic substances by macrophages, fibroblasts, and endothelial cells. On B cells, it promotes cellular activation, immunoglobulin class switching to IgE, and the up-regulation of CD23/Fc epsilon RII (1, 5). IL-13
binds with low affinity to the transmembrane IL-13 R alpha 1 which then forms a signaling complex with the transmembrane IL-4 R alpha (6-8). This high
affinity receptor complex also functions as the type 2 IL-4 receptor (6, 7). IL-13 R alpha 2 inhibits responses to both IL-13 and IL-4. It binds IL-13 with high affinity (9, 10) and prevents IL-13 from signaling through the IL-13 R alpha 1/IL-4 R alpha complex (11, 12). It also blocks signaling through IL-4-occupied
IL-13 R alpha 1/IL-4 R alpha receptor complexes (12, 13). In addition, IL-13-bound IL-13 R alpha 2 can directly promote tumor cell invasiveness and thedevelopment of tissue fibrosis (14-16).
1.Saggini, A. et al. (2011) Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 24:305.
2. Gallo, E. et al. (2012) Eur. J. Immunol. 42:2322.
3. Liang, H.E. et al. (2012) Nat. Immunol. 13:58.
4. Ruetten, H. and C. Thiemermann (1997) Shock 8:409.
5. McKenzie, A.N. et al. (1993) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90:3735.
6. Aman, M.J. et al. (1996) J. Biol. Chem. 271:29265.
7. Zurawski, S.M. et al. (1995) J. Biol. Chem. 270:13869.
8. Andrews, A.L. et al. (2002) J. Biol. Chem. 277:46073.
9. Chen, W. et al. (2009) J. Immunol. 183:7870.
10. Daines, M.O. et al. (2007) J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 119:375.
11. Kasaian, M.T. et al. (2011) J. Immunol. 187:561.
12. Andrews, A.-L. et al. (2006) J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 118:858.
13. Rahaman, S.O. et al. (2002) Cancer Res. 62:1103.
14. Fujisawa, T. et al. (2009) Cancer Res. 69:8678.
15. Fujisawa, T. et al. (2011) Int. J. Cancer 131:344.
16. Fichtner-Feigl, S. et al. (2006) Nat. Med. 12:99.