Cat: HF-1017A
Cat: HF-1017A
IL17A, Human, HEK293 Cells,Tag Free: Product Information
Human IL17A; hIL-17A, recombinant IL17A, interleukin 17A
Q16552
Human embryonic kidney cell, HEK293-derived human IL17A proteinGly24-Ala155
15.1 kDa (Monomer)
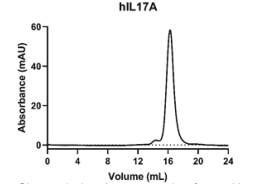
Dimer in solution
Solution protein.
Dissolved in sterile PBS buffer.
This solution can be diluted into other aqueous buffers. Centrifuge the vial prior to opening.
Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
Shipping with dry ice.
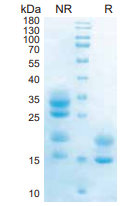
> 95%, determined by SDS-PAGE.
<0.010 EU per 1 ug of the protein by the LAL method.
Measured by its ability to induce IL-6 secretion by NIH-3T3 mouse embryonic fibroblast cells. The ED50 for this effect is 1.0-7.5 ng/mL.
IL17A, Human, HEK293 Cells,Tag Free:SDS-PAGE & Bioactivity
IL17A, Human, HEK293 Cells,Tag Free:Synonyms
Human IL17A; hIL-17A, recombinant IL17A, interleukin 17A
IL17A, Human, HEK293 Cells,Tag Free:Background
Interleukin-17A (IL-17A), also known as CTLA-8, is a 15-20 kDa glycosylated cytokine that plays an important role in anti-microbial and chronic inflammation. The six IL-17 cytokines (IL-17A-F) are encoded by separate genes but adopt a conserved cystine knot fold (1, 2). Mature human IL-17A shares 60% amino acid sequence identity with mouse and rat IL-17A (3, 4). IL-17A is secreted by Th17 cells, gamma /δ T cells, iNKT cells, NK cells, LTi cells, neutrophils, and intestinal Paneth cells (2). It forms disulfide-linked homodimers as well as disulfide-linked heterodimers with IL-17F (5, 6). IL-17A exerts its effects through the transmembrane IL-17RA in complex with IL-17RC or IL-17RD (7, 8). Both IL-17RA and IL-17RC are required for responsiveness to heterodimeric IL-17A/F (7). IL-17A promotes protective mucosal and epidermal inflammation in response to microbial infection (9-12). It induces chemokine production, neutrophil influx, and the production of antibacterial peptides (9-11). IL-17A/F likewise induces neutrophil migration, but IL-17F does not (11). IL-17A additionally enhances the production of inflammatory mediators by rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts and contributes to TNF-alpha induced shock (4, 13). In contrast, it can protect against the progression of colitis by limiting chronic inflammation (12). IL-17A has been shown to exert either tumorigenic or anti-tumor effects (14, 15).
1. Gaffen, S.L. (2009) Nat. Rev. Immunol. 9:556.
2. Cua, D.J. and C.M. Tato (2010) Nat. Rev. Immunol. 10:479.
3.Yao, Z. et al. (1995) J. Immunol. 155:5483.
4. Fossiez, F. et al. (1996) J. Exp. Med. 183:2593.
5. Chang, S.H. and C. Dong (2007) Cell Res. 17:435.
6. Wright, J.F. et al. (2007) J. Biol. Chem. 282:13447.
7. Wright, J.F. et al. (2008) J. Immunol. 181:2799.
8. Rong, Z. et al. (2009) Cell Res. 19:208.
9. Cho, J.S. et al. (2010) J. Clin. Invest. 120:1762.
10. Liang, S.C. et al. (2006) J. Exp. Med. 203:2271.
11. Liang, S.C. et al. (2007) J. Immunol. 179:7791.
12. O’Connor Jr., W. et al. (2009) Nat. Immunol. 10:603.
13. Takahashi, N. et al. (2008) J. Exp. Med. 205:1755.
14. Wang, L. et al. (2009) J. Exp. Med. 206:1457.
15. Kryczek, I. et al. (2009) Blood 114:357.