Cat: HF-1008
Cat: HF-1008
IL8, Human, HEK293 Cells,Tag Free: Product Information
3-10C; AMCF-I; C-X-C motif chemokine 8; CXCL8; CXCL8SCYB8; Emoctakin; GCP1;IL8;
P10145.1
Human embryonic kidney cell, HEK293-derived human IL-8/CXCL8 protein
Ser28-Ser99
8.5 kDa
Solution protein
Dissolved in sterile PBS buffer.
This solution can be diluted into other aqueous buffers. Centrifuge the vial prior to opening.
Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
Shipping with dry ice.
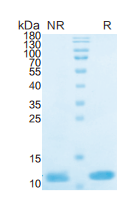
> 95%, determined by SDS-PAGE.
<0.010 EU per 1 ug of the protein by the LAL method.
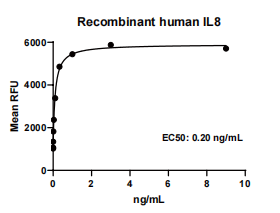
Measured by its ability to chemoattract BaF3 mouse pro-B cells transfected with human CXCR2. The ED50 for this effect is 0.2-1.0 ng/mL.
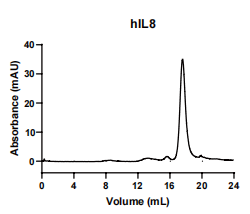
IL8, Human, HEK293 Cells,Tag Free:SDS-PAGE & Bioactivity
IL8, Human, HEK293 Cells,Tag Free:Synonyms
3-10C; AMCF-I; C-X-C motif chemokine 8; CXCL8; CXCL8SCYB8; Emoctakin; GCP1;IL8;
IL8, Human, HEK293 Cells,Tag Free:Background
Interleukin-8 (IL-8) , also known as CXCL8, GCP-1, and NAP-1, is a widely expressed proinflammatory member of the CXC family of chemokines. Near its N-terminus, this 8-9 kDa chemokine contains an ELR motif which is important for its angiogenic properties (1). IL-8/CXCL8 can associate into a homodimer or a heterodimer with CXCL4/PF4 (2), and it can also interact with matrix and cell surface glycosaminoglycans (3). Mature human IL-8/CXCL8 shares 65%-69% amino acid (aa) sequence identiity with canine, feline, and porcine IL-8/CXCL8 (4). There is no IL-8/CXCL8 gene counterpart in rodent. N-terminal truncation by multiple proteases generates a range of shorter forms, and an alternative splice form of human IL-8/CXCL8 carries an eleven aa substitution at the C-terminus (5). The bioactivity of IL-8/CXCL8 is regulated by these truncations, by IL-8/CXCL8 citrullination at Arg5 (N-terminal to the ELR motif) (6), and by the decoy receptor DARC (7). IL-8/CXCL8 effects are mediated through CXCR1/IL-8 RA, which is also used by CXCL6, and through CXCR2/IL-8 RB, which is used by multiple CXC chemokines (1). CXCR1 and CXCR2 associate into functional homodimers and heterodimers with each other (8). Through both CXCR1 and CXC R2, CXCL8 promotes neutrophil adhesion to the vascular endothelium and migration to sites of inflammation (9). It triggers the antimicrobial activation of neutrophils through CXCR1 (10).
1. Lazennec, G. and A. Richmond (2010) Trends Mol. Med. 16:133.
2. Nesmelova, I.V. et al. (2005) J. Biol. Chem. 280:4948.
3. Pichert, A. et al. (2012) Biomatter 2:142.
4. Schmid, J. and C. Weissmann (1987) J. Immunol. 139:250.
5. Mortier, A. et al. (2008) Pharmacol. Ther. 120:197.
6. Proost, P. et al. (2008) J. Exp. Med. 205:2085.
7. Neote, K. et al. (1994) Blood 84:44.
8. Munoz, L.M. et al. (2009) J. Immunol. 183:7337.
9. Gerszten, R.E. et al. (1999) Nature 398:718.
10. Jones, S.A. et al. (1996) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93:6682.