Cat: HF-1004
Cat: HF-1004
IL4, Human, HEK293 Cells,Tag Free: Product Information
Human IL4; hIL-4, recombinant IL4, interleukin 4, BCGF1 Protein
P05112
Human embryonic kidney cell, HEK293-derived human IL4 protein
His25-Ser153
15 kDa
Solution protein
Dissolved in sterile PBS buffer.
This solution can be diluted into other aqueous buffers. Centrifuge the vial prior to opening.
Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage.
12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
Shipping with dry ice.
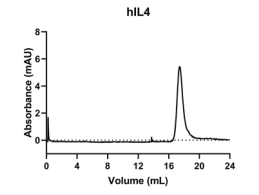
> 95%, determined by SDS-PAGE.
<0.010 EU per 1 ug of the protein by the LAL method.
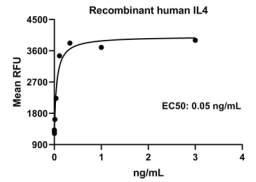
Measured in a cell proliferation assay using TF-1 human erythroleukemic cells.
The EC50 for this effect is 0.02-0.1 ng/mL.
IL4, Human, HEK293 Cells,Tag Free:SDS-PAGE & Bioactivity
IL4, Human, HEK293 Cells,Tag Free:Synonyms
Human IL4; hIL-4, recombinant IL4, interleukin 4, BCGF1 Protein
IL4, Human, HEK293 Cells,Tag Free:Background
Interleukin-4 (IL-4), also known as B cell-stimulatory factor-1, is a secreted protein that belongs to the IL-4 / IL-13 family (1-3). It is a glycosylated polypeptide that contains three intrachain disulfide bridges and adopts a bundled four α-helix structure (4). Mature human IL-4 shares 55%, 39% and 43% aa sequence identity with bovine, mouse, and rat IL-4, respectively. Human, mouse, and rat IL-4 are species-specific in their activities (5-7). IL-4 exerts its effectsthrough two receptor complexes (8, 9). The type I receptor, which is expressed on hematopoietic cells, is a heterodimer of the ligand binding IL-4 Rα and thecommon γ chain (a shared subunit of the receptors for IL-2, -7, -9, -15, and -21). The type II receptor on nonhematopoietic cells consists of IL-4 Rα and IL-13 Rα1.The type II receptor also transduces IL-13 mediated signals. IL-4 is primarily expressed by Th2-biased CD4+ T cells, mast cells, basophils, and eosinophils (1, 2). Itpromotes cell proliferation, survival, and immunoglobulin class switch to IgG4 and IgE in human B cells, acquisition of the Th2 phenotype by naive CD4+ T cells, priming and chemotaxis of mast cells, eosinophils, and basophils, and the proliferation and activation of epithelial cells (10-13).
1. Benczik, M. and S.L. Gaffen (2004) Immunol. Invest. 33:109.
2. Chomarat, P. and J. Banchereau (1998) Int. Rev. Immunol. 17:1.
3. Yokota, T. et al. (1986) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 83:5894.
4. Redfield, C. et al. (1991) Biochemistry 30:11029.
5. Ramirez, F. et al. (1988) J. Immunol. Meth. 221:141.
6. Leitenberg, D. and T.L. Feldbush (1988) Cell. Immunol. 111:451.
7. Mosman, T.R. et al. (1987) J. Immunol. 138:1813.
8. Mueller, T.D. et al. (2002) Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1592:237.
9. Nelms, K. et al. (1999) Annu. Rev. Immunol. 17:701.
10. Paludan, S.R. (1998) Scand. J. Immunol. 48:459.
11. Corthay, A. (2006) Scand. J. Immunol. 64:93.
12. Ryan, J.J. et al. (2007) Crit. Rev. Immunol. 27:15.
13. Grone, A. (2002) Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 88:1.