Cat: HF-2020
Cat: HF-2020
VEGFA, Human, HEK293 Cells,Tag Free: Product Information
NP_001165097
Human embryonic kidney cell, HEK293-derived human VEGF protein
Ala27-Arg191
19.2 kDa(Monomer)
Disulfide-linked homodimer
Solution protein.
Dissolved in sterile PBS buffer. This solution can be diluted into other aqueous buffers. Centrifuge the vial prior to opening.
Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
Shipping with dry ice.
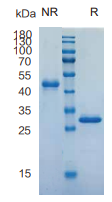
> 95%, determined by SDS-PAGE.
<0.010 EU per 1 ug of the protein by the LAL method.
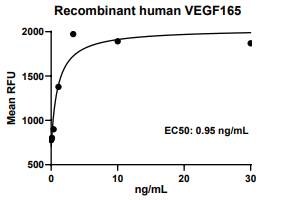
Measured in a cell proliferation assay using HUVEC human umbilical vein endothelial cells. The EC50 for this effect is 0.5-3 ng/mL.
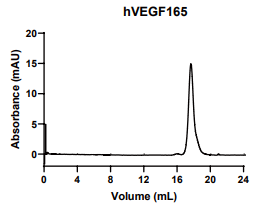
VEGFA, Human, HEK293 Cells,Tag Free:SDS-PAGE & Bioactivity
VEGFA, Human, HEK293 Cells,Tag Free:Synonyms
MVCD1; VAS; vascular endothelial growth factor A; Vascular permeability factor; VEGF; VEGFA
VEGFA, Human, HEK293 Cells,Tag Free:Background
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor(VEGF) is a potent growth factor that promotes both angiogenesis and vascular permeability (1-3). It acts
on endothelial cells by signaling primarily through two VEGF receptors, VEGF R1 (also called Flt-1) and VEGF R2 (Flk-1/KDR). VEGF's main responsibility
is to induce blood vessel formation during development and following tissue injury, and to bypass blocked blood vessels. During embryogenesis, VEGF
is required for proliferation, migration, and survival of endothelial cells (3, 4). In addition, VEGF also plays a role in several other physiological processes
such as hematopoiesis, bone formation, wound healing, and neuronal development. Pathologically, VEGF is involved in tumor angiogenesis and vascular leakage (6, 7), and it has been implicated as a major player in many different cancers, both solid tumors and hematopoietic malignancies. Circulating VEGF levels correlate with disease activity in autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis and systemic lupus erythematosus (8). VEGF expression is induced by hypoxia and cytokines such as IL-1, IL-6, IL-8, oncostatin M and TNF-alpha (3, 4, 9). Human VEGF165 shares 88% aa
sequence identity with corresponding regions of mouse and rat, 96% with porcine, 95% with canine, and 93% with feline, equine and bovine VEGF,
respectively. VEGF signals by binding to the type I transmembrane receptor tyrosine kinases VEGF R1 (also called Flt-1) and VEGF R2 (Flk-1/KDR) on endothelial cells (4). Although VEGF affinity is highest for binding to VEGF R1, VEGF R2 appears to be the primary mediator of VEGF angiogenic activity
(3, 4). VEGF 165 also binds the semaphorin receptor, Neuropilin-1 and promotes complex formation with VEGF R2 (5).
1. Leung, D.W. et al. (1989) Science 246:1306.
2. Keck, P.J. et al. (1989) Science 246:1309.
3. Byrne, A.M. et al. (2005) J. Cell. Mol. Med. 9:777.
4. Robinson, C.J. and S.E. Stringer (2001) J. Cell. Sci. 114:853.
5. Pan, Q. et al. (2007) J. Biol. Chem. 282:24049.
6. Weis, S.M. and D.A. Cheresh (2005) Nature 437:497.
7. Thurston, G. (2002) J. Anat. 200:575.
8. Carvalho, J.F. et al. (2007) J. Clin. Immunol. 27:246.
9. Angelo, L.S. and R. Kurzrock (2007) Clin. Cancer Res. 13:2825.