Cat: HF-2005
Cat: HF-2005
G-CSF/CSF3, Human, HEK293 Cells,Tag Free: Product Information
P09919
Human embryonic kidney cell, HEK293-derived human G-CSF/CSF3 protein
Thr31-Pro204
18.7 kDa
Solution protein.
Dissolved in sterile PBS buffer. This solution can be diluted into other aqueous buffers. Centrifuge the vial prior to opening.
Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage.12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
Shipping with dry ice
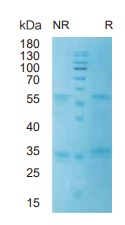
> 95%, determined by SDS-PAGE
<0.010 EU per 1 ug of the protein by the LAL method
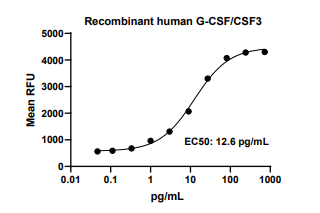
Measured in a cell proliferation assay using NFS-60 mouse myelogenous leukemia lymphoblast cells. The EC50 for this effect is 10-20 pg/mL.
G-CSF/CSF3, Human, HEK293 Cells,Tag Free:SDS-PAGE & Bioactivity
G-CSF/CSF3, Human, HEK293 Cells,Tag Free:Synonyms
C17orf33; colony stimulating factor 3 (granulocyte); CSF3; CSF3OS; Filgrastim; GCSF; G-CSF
G-CSF/CSF3, Human, HEK293 Cells,Tag Free:Background
Granulocyte Colony Stimulating Factor(G-CSF) is a pleiotropic cytokine best known for its specific effects on the proliferation, differentiation,
and activation of hematopoietic cells of the neutrophilic granulocyte lineage. It is produced mainly by monocytes and macrophages upon activation by
endotoxin, TNF-alpha and IFN-gamma. Other cell types including fibroblasts, endothelial cells, astrocytes and bone marrow stromal cells can also
secrete G-CSF after LPS, IL-1 or TNF-alpha activation. In addition, various carcinoma cell lines and myeloblastic leukemia cells can express G-CSF
constitutively. In humans, two distinct cDNA clones for G-CSF, encoding 207 and 204 amino acid precursor proteins, have been isolated. Both proteins have a 30 amino acid signal peptide and have identical amino acid sequences except for a three amino acid insertion (deletion) at the 35th amino acid
residue from the N-terminus of the mature protein. Human G-CSF is 73% identical at the amino acid level to murine G-CSF and the two proteins show species cross-reactivity. In vitro, G-CSF stimulates growth, differentiation and functions of cells from the neutrophil lineage. It also has blast cell growth factor activity and can synergize with IL-3 to shorten the Go period of early hematopoietic progenitors. Consistent with its in vitro functions, G-CSF has been found to play important roles in defense against infection, in inflammation and repair, and in the maintenance of steady state hematopoiesis.
1. Takano H, et al. (2007) Trends Pharmacol Sci. 28(10): 512-7
2. Klocke R, et al. (2008) Curr Med Chem. 15(10): 968-77.
3. Kang HJ, et al. (2008) Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther. 6(5): 703-13.
4. Beekman R, et al. (2010) Blood. 115(25): 5131-6.