Cat: MF-2014
Cat: MF-2014
HGF, Mouse, ,Tag Free: Product Information
Measured in a cell proliferation assay using mIMCD-3 mouse epithelial cells.
The EC50 for this effect is 1-10 ng/mL.
<0.010 EU per 1 ug of the protein by the LAL method
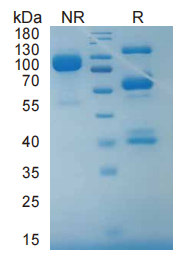
> 95%, determined by SDS-PAGE
Shipping with dry ice
Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage.
12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
Solution protein
Dissolved in sterile PBS buffer .
This solution can be diluted into other aqueous buffers. Centrifuge the vial prior to opening.
79.3kDa
Human embryonic kidney cell, HEK293-derived mouse HGF protein
Gln33-Arg495 (alpha) & Val496-Leu728 (beta)
Q08048
F-TCF; hepatocyte growth factor (hepapoietin A; scatter factor); Hepatopoeitin-A; Hepatopoietin A; HGF
HGF, Mouse, ,Tag Free:Synonyms
F-TCF; hepatocyte growth factor (hepapoietin A; scatter factor); Hepatopoeitin-A; Hepatopoietin A; HGF
HGF, Mouse, ,Tag Free:Background
Hepatocyte Growth Factor(HGF), also known as Scatter Factor and Hepatopoietin A, is a pleiotropic protein in the Plasminogen subfamily of S1 peptidases. It is a multidomain molecule that includes an N-terminal PAN/APPLE-like domain, four Kringle domains, and a serine proteinase-like domain that has no detectable protease activity (1 - 5). Mouse HGF is secreted as an inactive 728 amino acid (aa) single chain propeptide. It is cleaved after the fourth Kringle domain by a serine protease to form bioactive disulfide-linked HGF with a 60 kDa alpha and 30 kDa beta chain. Alternate splicing generates an isoform that lacks the peptidase and the second, third, and fourth Kringle domains. Mouse HGF shares 91% - 95% aa sequence identity with bovine, canine, feline, human, and rat HGF. HGF binds heparan-sulfate proteoglycans and the widely expressed receptor tyrosine kinase, HGF R/c-MET (6, 7). HGF-dependent c-MET activation is implicated in the development of many human cancers (8). HGF regulates epithelial morphogenesis by inducing cell scattering and branching tubulogenesis (9, 10). HGF induces the up-regulation of integrin alpha 2 beta 1 in epithelial cells by a selective increase in alpha 2 gene transcription (11). This integrin serves as a collagen I receptor, and its blockade disrupts epithelial cell branching tubulogenesis (11, 12). HGF can also alter epithelium morphology by the induction of nectin-1 alpha ectodomain shedding, an adhesion protein component of adherens junctions (13). In the thyroid, HGF induces the proliferation, motility, and loss of differentiation markers of thyrocytes and inhibits TSH-stimulated iodine uptake (14).
1. Karihaloo, A. et al. (2005) Nephron Exp. Nephrol. 100:e40.
2. Hammond, D.E. et al. (2004) Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 286:21.
3. Rosario, M. and W. Birchmeier (2004) Dev. Cell 7:3.
4. Lesk, A.M. and W.D. Fordham (1996) J. Mol. Biol. 258:501.
5. Sasaki, M. et al. (1994) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 199:772.
6. Mizuno, K., et al. (1994) J. Biol. Chem. 269:1131.
7. Gheradi, E. et al. (2003) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 100:12039.
8. Corso, S. et al. (2005) Trends Mol. Med. 11:284.
9. Maeshima, A. et al. (2000) Kid. Int. 58:1511.
10. Montesano, R. et al. (1991) Cell 67:901.
11. Chiu, S-J. et al. (2002) J. Biomed. Sci. 9:261.
12. Saelman, E.U.M. et al. (1995) J. Cell Sci. 108:3531.
13. Tanaka, Y. et al. (2002) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 299:472.
14. Mineo, R. et al. (1994) Endocrinology 145:4355.