Cat: MF-2002
Cat: MF-2002
LIF, Mouse, HEK293 Cells,Tag Free: Product Information
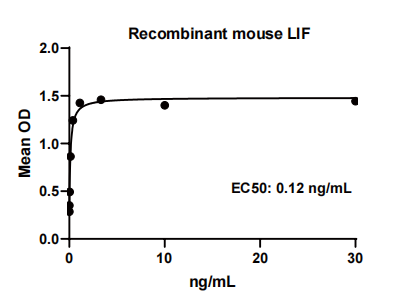
Measured by its ability to induce IL-6 secretion by M1 mouse myeloid leukemia cells.
The EC50 for this effect is 0.05-0.2 ng/mL
<0.010 EU per 1 ug of the protein by the LAL method
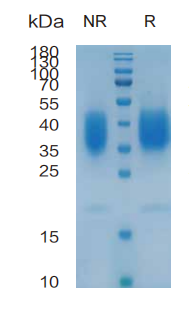
> 95%, determined by SDS-PAGE
Shipping with dry ice
Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage.
12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
Solution protein
Dissolved in sterile PBS buffer.
This solution can be diluted into other aqueous buffers. Centrifuge the vial prior to opening.
20 kDa
Human embryonic kidney cell, HEK293-derived mouse LIF protein
Pro25-Phe203
P09056
leukemia inhibitory factor; LIF;CDF; D Factor; DIA; differentiation inhibitory activity
LIF, Mouse, HEK293 Cells,Tag Free:SDS-PAGE & Bioactivity
LIF, Mouse, HEK293 Cells,Tag Free:Synonyms
leukemia inhibitory factor; LIF;CDF; D Factor; DIA; differentiation inhibitory activity
LIF, Mouse, HEK293 Cells,Tag Free:Background
Recombinant mouse LIF (leukemia inhibitory factor) is commonly used in cell culture to maintain the pluripotency of stem cells. LIF is a widely expressed pleiotropic member of the IL-6 family of cytokines (1-3). Mature mouse LIF is expressed as a highly and variably glycosylated 32-62 kDa monomer that shares 78%, 91%, 80%, 76%, and 78% aa sequence identity with human, rat, canine, bovine, and porcine LIF, respectively (4). LIF functions through a heterodimeric receptor complex containing a ligand-binding subunit, LIF R alpha /CD118, and a signal transducing subunit, gp130 (2, 4, 5). gp130 also serves as a subunit of the receptor complexes for Oncostatin M, Cardiotrophin-1, CNTF, IL-6, IL-11, and IL-27 (2, 5). A soluble form of mouse LIF R alpha can be generated by alternative splicing (6). Depending on the cells and their context, LIF either opposes or favors differentiation (2, 7). LIF produced by the uterine endometrium supports successful implantation of the embryo, promotes proliferation and maintenance of pluripotency in embryonic stem cells, and favors proliferation of progenitor cell types such as hematopoietic stem cells (2, 5, 7). LIF can also function as an autocrine growth factor in some pancreatic cancers, but it induces differentiation in the myeloid leukemic cell line M1 (1, 8). Tumor cell-derived LIF can also induce formation of immunosuppressive tumor-associated macrophages (9). LIF promotes endometrial remodeling and differentiation of adipocytes and cardiac smooth muscle cells (2, 3, 10). It promotes regulatory T cell and inhibits Th17 cell differentiation, thus down-regulating inflammation and contributing to immune tolerance during pregnancy and in the nervous system (2, 3, 5, 7).
1. Moreau, J.F. et al. (1988) Nature 336:690.
2. Trouillas, M. et al. (2009) Eur. Cytokine Netw. 20:51.
3. Metcalfe, S.M. (2011) Genes Immun. 12:157.
4. Gearing, D.P. et al. (1987) EMBO J. 6:3995.
5. Cheng, J.G. et al. (2001) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98:8680.
6. Tomida, M. et al. (1993) FEBS lett. 334:193.
7. Paiva, P. et al. (2009) Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 20:319.
8. Kamohara, H. et al. (2007) Int. J. Oncol. 30:977.
9. Duluc, D. et al. (2007) Blood 110:4319.
10. Zouein, F.A. et al. (2013) Eur. Cytokine Netw. 24:11.